How many neurons are in the brain? This intriguing question lies at the heart of understanding the complex organ that governs our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Join us as we delve into the neural composition of the brain, exploring the types of neurons, their functions, and the factors that influence their count.
We’ll uncover the methods used to estimate neuron count, from historical approaches to modern techniques, and examine the similarities and differences in neuron count across animal models and humans.
Understanding the number of neurons in the brain is not just a matter of scientific curiosity; it holds significant implications for neuroscience research and clinical practice. It can shed light on the development of neurological disorders, the effects of aging on brain function, and the potential for brain repair and regeneration.
As we unravel the mysteries of neuron count, we unlock a deeper understanding of the brain’s intricate workings and pave the way for advancements in brain-related healthcare.
Neural Composition of the Brain: How Many Neurons Are In The Brain
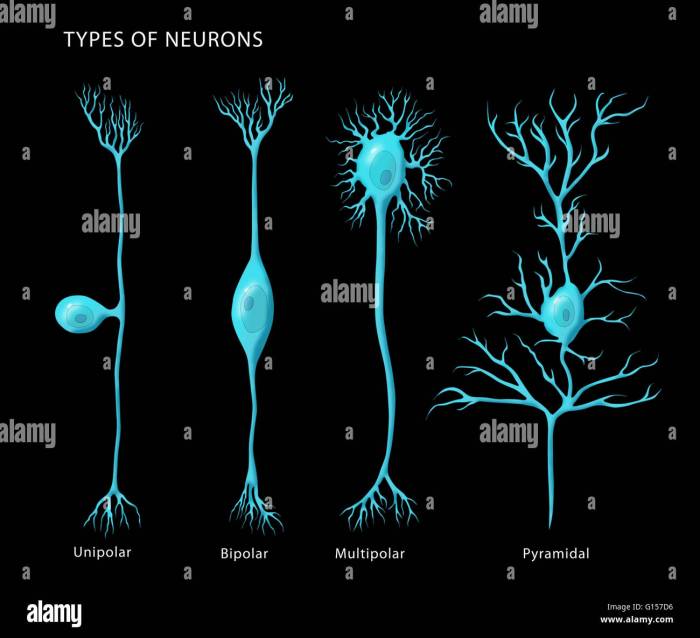
The brain, the central organ of the nervous system, is composed of billions of neurons, each with its unique structure and function. Understanding the neural composition of the brain provides insights into its intricate operations and capabilities.
Primary Types of Neurons
- Sensory Neurons:Transmit sensory information from the body to the brain.
- Motor Neurons:Carry signals from the brain to muscles and glands, controlling movement.
- Interneurons:Connect neurons within the brain, processing and relaying information.
Brain Regions and Neuron Counts, How many neurons are in the brain
Different brain regions vary in neuron count, reflecting their specific functions:
- Cerebral Cortex:Contains the highest number of neurons (approximately 14 billion), responsible for complex cognitive functions.
- Cerebellum:Coordinates movement and balance, with approximately 100 billion neurons.
- Hippocampus:Plays a crucial role in memory formation, containing about 20 million neurons.
Factors Influencing Neuron Count
The number of neurons in the brain is influenced by several factors:
- Genetics:Inherited traits contribute to brain size and neuron count.
- Environment:Enriching experiences, such as education and social interaction, can stimulate neuron growth.
- Age:Neuron count typically decreases with age, especially in certain brain regions.
Methods for Estimating Neuron Count
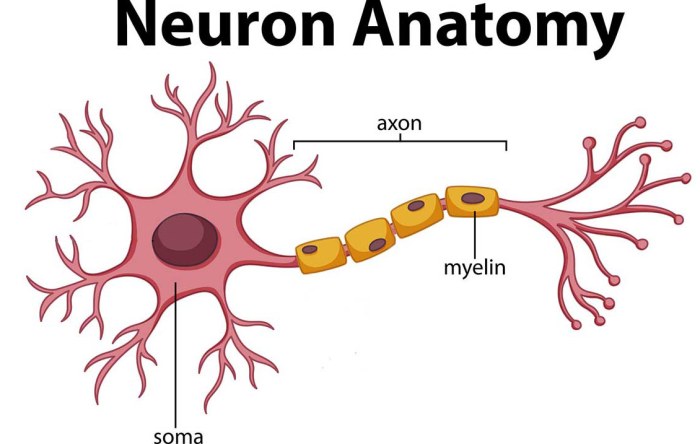
Determining the exact number of neurons in the brain has been a longstanding challenge in neuroscience. Over the years, scientists have developed various methods to estimate this vast number, ranging from historical techniques to modern computational approaches.
Historical Methods
Early attempts to count neurons relied on manual counting under a microscope. Researchers would physically dissect brain tissue into thin sections and stain the neurons to make them visible. They would then painstakingly count the neurons under a microscope, often using a grid to ensure accuracy.
Modern Techniques
Modern methods for estimating neuron count have become increasingly sophisticated, employing advanced technologies and computational algorithms.
Stereology
Stereology is a specialized technique that involves sampling a small portion of brain tissue and extrapolating the neuron count to the entire brain. This method uses a series of mathematical equations and statistical techniques to estimate the total number of neurons based on the density of neurons in the sample.
Computational Approaches
Computational approaches, such as machine learning and image analysis, have also been employed to count neurons. These techniques utilize high-resolution images of brain tissue to identify and count neurons automatically. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize neurons based on their shape, size, and other characteristics.
Comparison of Methods
Each method for estimating neuron count has its own advantages and limitations.
- Accuracy:Stereology is generally considered the most accurate method, but it can be time-consuming and requires specialized expertise.
- Efficiency:Computational approaches can be more efficient, but their accuracy can vary depending on the quality of the images and the training data used.
- Applicability:Historical methods are limited to small brain samples, while stereology and computational approaches can be applied to larger samples or even whole brains.
Despite the advances in neuron counting techniques, the exact number of neurons in the human brain remains a matter of debate. However, these methods have provided valuable insights into the complexity and organization of the human brain.
Animal Model Studies
To understand the complexities of the human brain, researchers often rely on animal models to estimate neuron count. Studies in various species have provided valuable insights into the number and distribution of neurons in different brain regions.
Animal model studies have revealed striking similarities and differences in neuron count across species. For instance, studies in mice have shown that the cerebral cortex contains approximately 70 million neurons, while in rats, the number is estimated to be around 200 million.
Mouse Studies
In mice, the cerebral cortex is composed of approximately 70 million neurons, distributed across six layers. The most numerous neurons are pyramidal cells, which account for about 80% of the total population. Other types of neurons include interneurons, which play a crucial role in regulating the activity of pyramidal cells.
Rat Studies
Rat studies have estimated that the cerebral cortex contains around 200 million neurons, significantly higher than in mice. The increased neuron count in rats is attributed to the larger size of their brains and the presence of a more complex cortical structure.
Implications for Human Brain Neuron Count
While animal model studies provide valuable information, it is important to note that the human brain is far more complex than that of any animal model. Therefore, direct extrapolation of neuron count estimates from animal models to humans should be done with caution.
Nevertheless, animal model studies have helped establish a foundation for understanding the organization and function of the human brain. By comparing neuron count estimates across species, researchers can gain insights into the evolutionary trajectory of the brain and the unique features that characterize the human brain.
Human Brain Neuron Count
The human brain is a complex organ, and one of the most important aspects of its complexity is the number of neurons it contains. Neurons are the basic units of the brain, and they are responsible for transmitting information throughout the organ.
The number of neurons in the human brain is estimated to be around 86 billion, give or take 8 billion.
The number of neurons in the human brain varies from region to region. The cerebral cortex, which is the outermost layer of the brain, contains the most neurons, with an estimated 14 billion neurons. The cerebellum, which is located at the back of the brain, contains an estimated 69 billion neurons.
The brainstem, which is located at the base of the brain, contains an estimated 3 billion neurons.
The number of neurons in the human brain is not fixed. It can change over time, due to factors such as age, gender, and neurological conditions. For example, the number of neurons in the human brain decreases with age. This decrease is most pronounced in the cerebral cortex, where the number of neurons can decrease by as much as 10% per decade after the age of 20.
The number of neurons in the human brain is also affected by gender. Men have an estimated 4% more neurons in their brains than women. This difference is most pronounced in the cerebral cortex, where men have an estimated 6% more neurons than women.
Neurological conditions can also affect the number of neurons in the human brain. For example, Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by the loss of neurons in the brain. Parkinson’s disease is another neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by the loss of neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain that is involved in movement.
Significance and Applications
Understanding the number of neurons in the brain is crucial for comprehending the brain’s structure and function. It provides insights into the brain’s processing capacity, cognitive abilities, and potential for neural plasticity. Neuron counting aids in assessing brain development, aging, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Neuroscience Research
Neuron count enables researchers to study the relationship between brain size, neuronal density, and cognitive function. It helps determine how the brain processes information, stores memories, and regulates behavior. By comparing neuron counts in different brain regions, scientists can identify areas responsible for specific cognitive functions and neural circuits.
Clinical Practice
In clinical practice, neuron counting aids in diagnosing and monitoring neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Reduced neuron count in specific brain regions can indicate the severity of the disease and help predict its progression. Neuron counting can also assist in assessing the efficacy of treatments and therapies for neurodegenerative conditions.
Areas for Further Research
Despite significant advancements, further research is needed to refine neuron counting methods and improve our understanding of the brain’s neural composition. Future studies should focus on:
- Developing more accurate and reliable neuron counting techniques.
- Investigating the relationship between neuron count and cognitive function in different brain regions.
- Exploring the role of neuron count in neurodevelopmental disorders and psychiatric illnesses.
- Understanding the impact of environmental factors and lifestyle choices on neuron count and brain health.
Wrap-Up
Our exploration into how many neurons are in the brain has revealed the immense complexity and diversity of the human brain. The number of neurons varies across brain regions, species, and individuals, influenced by a multitude of factors. While we’ve made significant progress in estimating neuron count, further research is needed to fully understand the implications of these variations and their impact on brain function and health.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the brain, the knowledge gained from neuron counting will undoubtedly contribute to groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in neuroscience and beyond.
Top FAQs
Why is it important to know how many neurons are in the brain?
Understanding neuron count provides insights into brain development, function, and health. It can help identify abnormalities associated with neurological disorders, assess the impact of aging on brain function, and guide strategies for brain repair and regeneration.
How do scientists estimate neuron count?
Neuron counting methods have evolved over time. Historically, researchers used manual counting techniques involving tissue staining and microscopy. Modern approaches include stereology, which involves sampling and statistical analysis, and computational methods that utilize advanced imaging techniques.
Do different brain regions have different neuron counts?
Yes, neuron count varies across brain regions. For example, the cerebral cortex, responsible for higher-level functions like cognition and language, has a higher neuron density compared to the brainstem, which controls basic functions like breathing and heart rate.
How does neuron count change over time?
Neuron count generally decreases with age, particularly in certain brain regions. This age-related decline may contribute to cognitive and functional changes associated with aging.
Can neuron count be affected by external factors?
Yes, environmental factors like stress, nutrition, and physical activity can influence neuron count. For example, chronic stress has been linked to reduced neuron production in the hippocampus, a brain region involved in memory and learning.